
Get Started with glyanno
glyanno.RmdThe Challenge
Mass spectrometry-based glycomics and glycoproteomics often yield data with limited structural resolution. For example, MALDI-TOF MS-based glycomics typically provides only m/z values, while many LC-MS/MS-based glycoproteomics workflows identify basic glycan compositions but lack isomer specificity. Mass spectrometry alone frequently fails to distinguish specific monosaccharide isomers (e.g., differentiating Mannose from Galactose), or resolve linkage details (e.g., a1-3 vs b1-4).
In theory, full structural resolution is achievable by combining MS with orthogonal techniques such as enzymatic digestion or NMR; however, these approaches are often resource-intensive and time-consuming. Unfortunately, advanced downstream analyses—such as the glycan biosynthetic pathway reconstruction offered by glyenzy— require fully resolved glycan structures, including specific monosaccharide identities and linkage information.
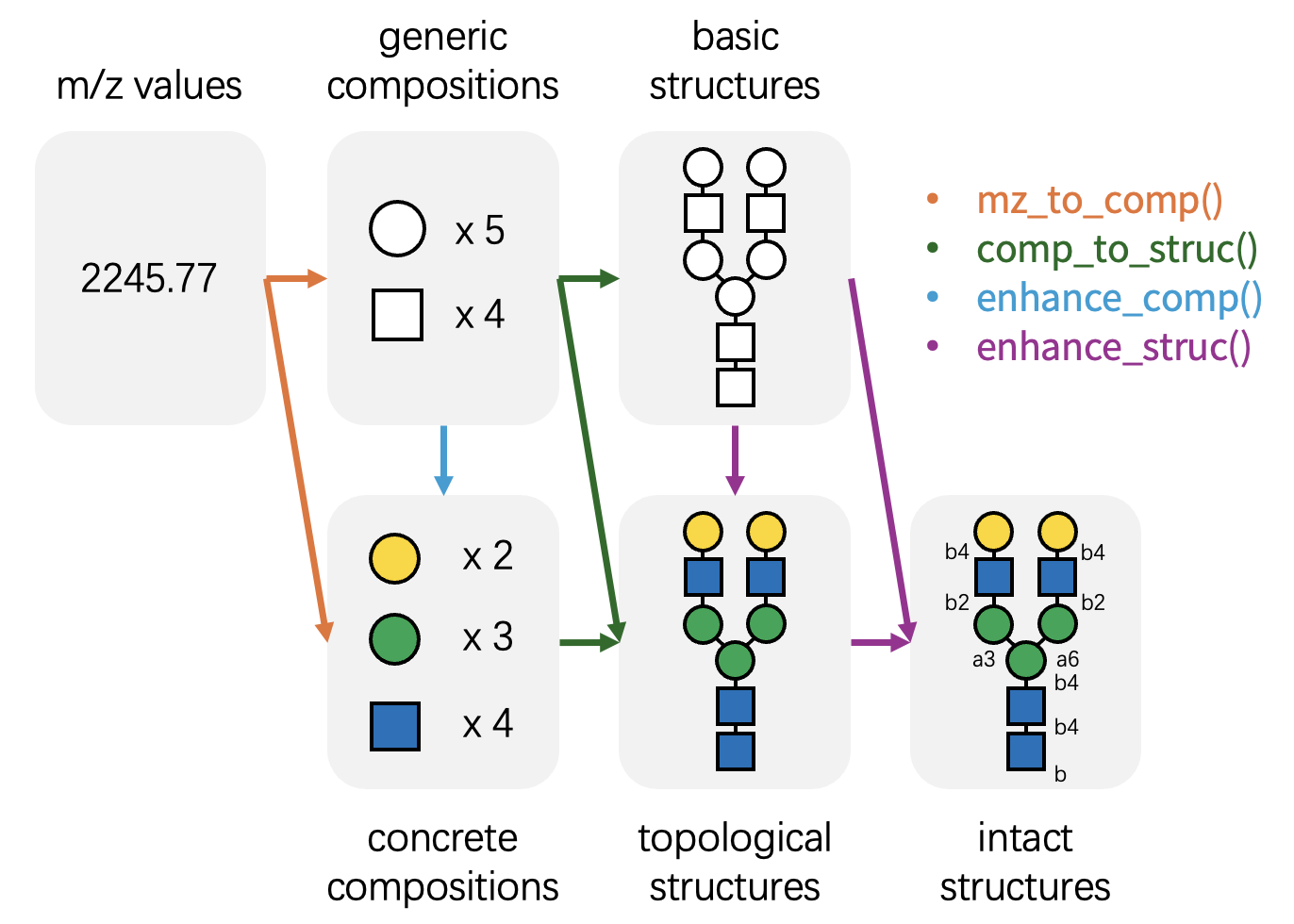
What is glyanno?
glyanno bridges this gap. This package is designed to
maximize the utility of your mass spectrometry data by annotating it
with probable biological context derived from knowledge bases. The
package features four core functions:
-
mz_to_comp(): Identifies possible glycan compositions from m/z values. -
comp_to_struc(): Maps glycan compositions to potential glycan structures. -
enhance_comp(): Refines generic glycan compositions into concrete, monosaccharide-specific compositions. -
enhance_struc(): Resolves low-resolution glycan structures into high-resolution structures with linkage information.
Note: This package relies on glyrepr and glydb. We recommend
familiarizing yourself with these packages, especially
glyrepr, before using glyanno. Additionally, a
basic understanding of IUPAC-condensed notation is recommended for this
vignette. You can refer to this tutorial.
Workflow: M/z -> Composition -> Structure
Let’s demonstrate these functions step-by-step, starting with a single m/z value.
mz_to_comp(406.1325, charge = 1, adduct = "Na+")
#> # A tibble: 4 × 2
#> mz composition
#> <dbl> <comp>
#> 1 406. Gal(1)GalNAc(1)
#> 2 406. Gal(1)GlcNAc(1)
#> 3 406. Glc(1)GlcNAc(1)
#> 4 406. Man(1)GlcNAc(1)This returns every composition in glydb matching the m/z
of 406.1325. In practice, returning “all” possibilities can be
overwhelming; you will often want to constrain the search space based on
biological context.
glydb provides helper functions to filter the database.
For example, you might want to limit the search to only human O-GalNAc
glycans.
my_db <- glydb_compositions(species = "Homo sapiens", glycan_type = "O-GalNAc")
my_db
#> <glycan_composition[128]>
#> [1] Gal(1)GalNAc(1)
#> [2] Gal(1)GlcNAc(1)GalNAc(1)
#> [3] GlcNAc(1)GalNAc(1)
#> [4] GlcNAc(2)GalNAc(1)
#> [5] GalNAc(2)
#> [6] Gal(2)GlcNAc(1)GalNAc(1)Neu5Ac(1)
#> [7] Gal(1)GalNAc(2)Neu5Ac(2)
#> [8] Gal(1)GalNAc(1)Fuc(1)
#> [9] Gal(2)GlcNAc(2)GalNAc(2)Fuc(1)
#> [10] Gal(2)GlcNAc(1)GalNAc(1)
#> ... (118 more not shown)my_db is simply a
glyrepr::glycan_composition() vector. You can pass it to
the db argument of mz_to_comp() to filter
results.
mz_to_comp(406.1325, charge = 1, adduct = "Na+", db = my_db)
#> # A tibble: 1 × 2
#> mz composition
#> <dbl> <comp>
#> 1 406. Gal(1)GalNAc(1)The results are now significantly more relevant to our specific context.
With the composition identified, we can proceed to determine potential structures. The m/z value 406.1325 corresponds to the composition Gal(1)GalNAc(1). What are the possible structures for this composition?
comp_to_struc(
"Gal(1)GalNAc(1)",
db = glydb_structures(species = "Homo sapiens", glycan_type = "O-GalNAc")
)
#> # A tibble: 2 × 2
#> composition structure
#> <comp> <struct>
#> 1 Gal(1)GalNAc(1) Gal(b1-3)GalNAc(a1-
#> 2 Gal(1)GalNAc(1) Gal(a1-3)GalNAc(a1-Note that here we use glydb_structures() instead of
glydb_compositions() to create a structure-specific
database.
Enhancing Compositions and Structures
Researchers often need to refine generic annotations into more
specific ones. For instance, you may wish to convert generic
compositions into specific monosaccharide lists, or assign potential
linkages to a topology-only structure. enhance_comp() and
enhance_struc() are designed for this purpose.
Both functions return a tibble with two columns: raw
(the original input) and enhanced (the potential
high-resolution candidates).
enhance_comp("Hex(1)HexNAc(1)")
#> # A tibble: 4 × 2
#> raw enhanced
#> <comp> <comp>
#> 1 Hex(1)HexNAc(1) Gal(1)GalNAc(1)
#> 2 Hex(1)HexNAc(1) Gal(1)GlcNAc(1)
#> 3 Hex(1)HexNAc(1) Glc(1)GlcNAc(1)
#> 4 Hex(1)HexNAc(1) Man(1)GlcNAc(1)
enhance_struc("Gal(??-?)GalNAc(??-")
#> # A tibble: 9 × 2
#> raw enhanced
#> <struct> <struct>
#> 1 Gal(??-?)GalNAc(??- Gal(b1-3)GalNAc(a1-
#> 2 Gal(??-?)GalNAc(??- Gal(b1-3)GalNAc(b1-
#> 3 Gal(??-?)GalNAc(??- Gal(a1-3)GalNAc(b1-
#> 4 Gal(??-?)GalNAc(??- Gal(b1-4)GalNAc(b1-
#> 5 Gal(??-?)GalNAc(??- Gal(a1-6)GalNAc(a1-
#> 6 Gal(??-?)GalNAc(??- Gal(b1-6)GalNAc(a1-
#> 7 Gal(??-?)GalNAc(??- Gal(b1-6)GalNAc(b1-
#> 8 Gal(??-?)GalNAc(??- Gal(a1-3)GalNAc(a1-
#> 9 Gal(??-?)GalNAc(??- Gal(b1-4)GalNAc(a1-Similarly, providing a custom database will narrow down the results to biologically relevant candidates.
enhance_comp("Hex(1)HexNAc(1)", db = glydb_compositions(species = "Homo sapiens", glycan_type = "O-GalNAc"))
#> # A tibble: 1 × 2
#> raw enhanced
#> <comp> <comp>
#> 1 Hex(1)HexNAc(1) Gal(1)GalNAc(1)
enhance_struc("Gal(??-?)GalNAc(??-", db = glydb_structures(species = "Homo sapiens", glycan_type = "O-GalNAc"))
#> # A tibble: 2 × 2
#> raw enhanced
#> <struct> <struct>
#> 1 Gal(??-?)GalNAc(??- Gal(b1-3)GalNAc(a1-
#> 2 Gal(??-?)GalNAc(??- Gal(a1-3)GalNAc(a1-Bidirectional Conversion
While glyanno focuses on inferring high-resolution
information from low-resolution data, the glycoverse
ecosystem also provides complementary functions to perform the reverse
operations—simplifying detailed structures back to their
lower-resolution representations.
A summary of these relationships:
| Enhance | Back |
|---|---|
mz_to_comp() |
calculate_mz() |
comp_to_struc() |
glyrepr::as_glycan_composition() |
enhance_comp() |
glyrepr::convert_to_generic() |
enhance_struc() |
glyrepr::reduce_structure_level() |